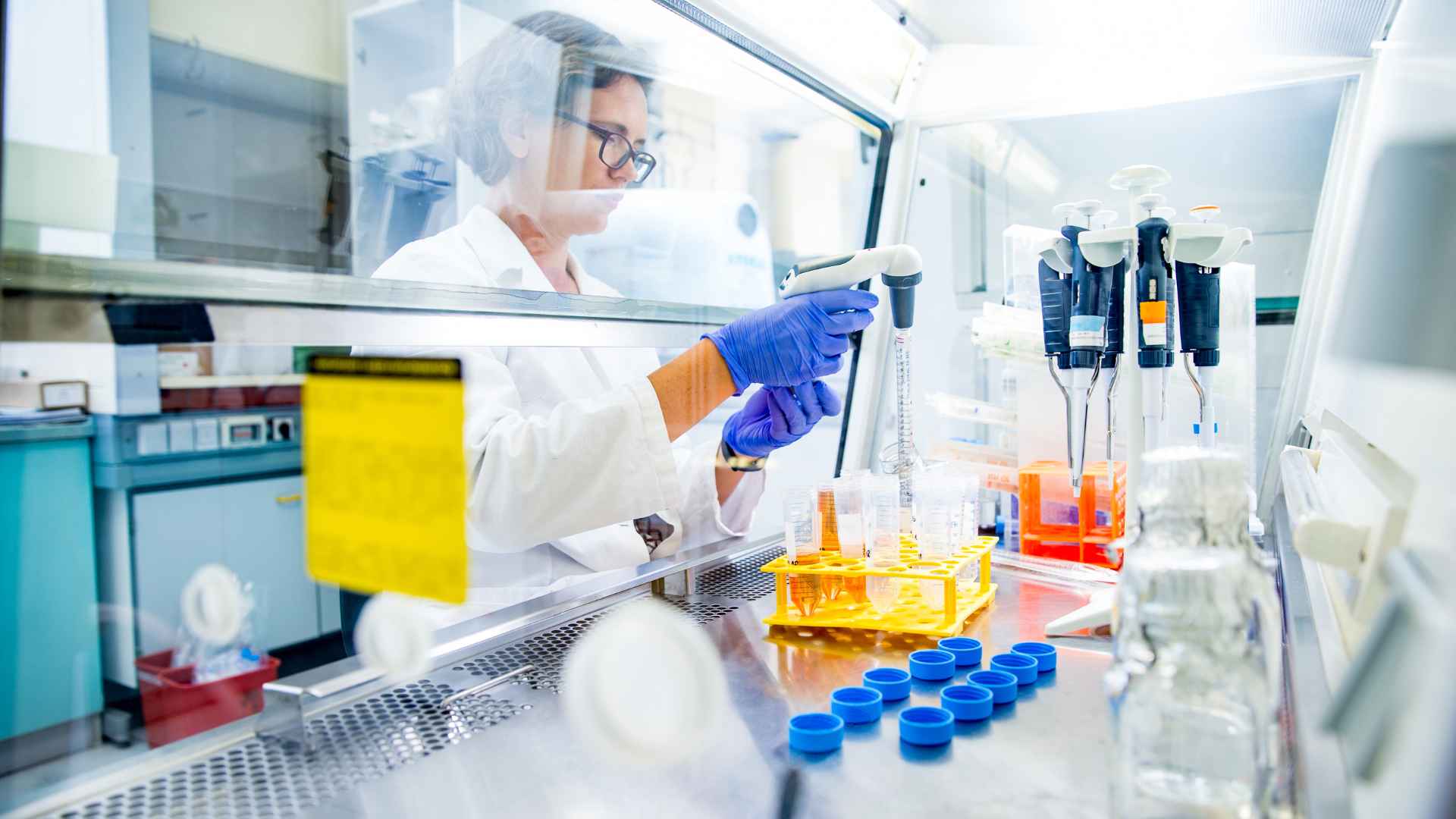
In the area of biomedical research, in vitro cell-based assays stand as a cornerstone, offering a window into the cellular response to various stimuli. These assays allow scientists to meticulously analyze the effects of drugs, toxins, and other substances on cells in a controlled environment, bridging the gap between molecular studies and in vivo experimentation.
With their ability to mimic biological processes within the confines of a petri dish, in vitro cell-based assays have revolutionized the way researchers approach the study of disease mechanisms, drug discovery, and toxicity testing. They’ve become an indispensable tool in the arsenal of modern science, enabling advancements that were once thought to be beyond reach.
Importance of In Vitro Cell-Based Assays
In vitro cell-based assays have become indispensable in the area of biomedical research, offering a versatile and efficient approach to understanding the complex interactions within biological systems. These assays use living cells to evaluate the effects of various substances, from drugs to toxins, providing invaluable insights into cellular responses, mechanisms of disease, and potential therapeutic effects.
Da-Ta Biotech, a pioneer in the field, harnesses the power of cell-based assays to propel the biotechnology industry forward. With over two dozen human and rodent cell lines at their disposal, researchers can jump into a plethora of disease models, significantly expanding the breadth of possible studies. The company’s in-house testing capabilities include models crucial for drug discovery and toxicity testing, such as those used for determining the EC50 of anti-cancer drugs and measuring the rate of wound healing.
Adaptability is a key feature of Da-Ta Biotech’s offerings. Beyond utilizing robust in-house protocols, the company can adapt researchers’ suggested SOPs/protocols, striking a balance between standardization and customization. This flexibility not only enhances the assay’s relevance to specific research needs but also substantially reduces costs and time associated with setting up independent laboratories.
Under the guidance of Dr. Rinat Borenshtain-Koreh and her experienced R&D team, Da-Ta Biotech supports researchers from the initial discovery phase through to investor presentations. This comprehensive support streamlines the path from conceptualization to real-world application, ensuring that advancements in cell-based assay technologies are both rapid and impactful.
In sum, the importance of in vitro cell-based assays in advancing our understanding of complex biological processes and facilitating drug development cannot be overstated. Through tailored protocols, a wide array of disease models, and expert guidance, Da-Ta Biotech exemplifies how cell-based assays are driving innovation within the biotechnology sector.
Applications in Disease Mechanisms Study
Da-Ta Biotech, through its use of in vitro cell-based assays, has become a pivotal player in unveiling mechanisms behind various diseases. Their cell-based assays provide a crucial window into how diseases evolve and how they can be potentially halted. This methodology stands at the forefront for researchers aiming to dissect the complex interplay between biological processes and disease pathogenesis.
By employing a vast array of human and rodent cell lines, Da-Ta Biotech crafts scenarios that mimic disease environments, allowing for the in-depth study of disease progression. This is particularly valuable in the field of oncology, where understanding the intricacies of cancer cell behavior is vital. In vitro cell-based assays serve as a reliable platform for observing the impacts of potential therapeutic compounds on cancer cells, in real-time.
One notable model utilized by Da-Ta Biotech in these assays is designed for screening anti-cancer drugs. This model aids in determining the EC50 (half maximal effective concentration), a critical value that measures a drug’s potency in inhibiting a specific biological or biochemical function. Such precise measurements pave the way for developing more effective, targeted cancer treatments.
Apart from oncology, these assays are instrumental in the study of wound healing. Da-Ta Biotech’s model for measuring the rate of wound healing under various conditions and treatments presents a promising avenue for discovering and testing new wound care solutions. By closely replicating the wound environment in vitro, researchers can observe the effectiveness of treatments in stimulating or inhibiting cell migration and proliferation, essential components of the wound-healing process.
The versatility of in vitro cell-based assays extends beyond these applications, encompassing a wide range of disease models. Da-Ta Biotech, under the guidance of experienced R&D specialists led by Dr. Rinat Borenshtain-Koreh, remains at the cutting edge of using cell-based assays to investigate into disease mechanisms. Their approach not only accelerates the pace of research from discovery through to application but also offers a cost-effective alternative to setting up and running independent laboratories.
Role in Drug Discovery
In vitro cell-based assays, crucial tools in the arsenal of drug discovery, have profoundly revolutionized the pharmaceutical industry. By providing a controlled environment to study the effects of new compounds on living cells, these assays help a deeper understanding of drug mechanisms and safety profiles before moving to more complex in vivo studies. Da-Ta Biotech plays a pivotal role in this domain, leveraging its advanced in vitro technologies to bridge the gap between theoretical research and real-world applications.
At the core of Da-Ta Biotech’s offerings is a suite of cell-based assay platforms that serve a wide array of functions in drug discovery. Their in-house testing capabilities, encompassing over two dozen human and rodent cell lines, enable a comprehensive evaluation of drug candidates across various disease models. This versatility not only accelerates the initial screening process but also increases the likelihood of identifying efficacious and safer drugs.
One notable example is Da-Ta Biotech’s EC50 determination model for anti-cancer drugs. By assessing how different concentrations of a drug affect cancer cell viability, researchers can garner insights into a drug’s potency and therapeutic window early in the development phase. Similarly, their wound healing model offers valuable data on the regenerative potential of compounds, an area of keen interest for treatments targeting diabetic ulcers and other chronic wounds.
Da-Ta Biotech further differentiates itself through its flexible approach to research protocols. Whether choosing to employ the company’s robust in-house protocol or opting to have Da-Ta adapt an external standard operating procedure (SOP), clients can streamline their R&D efforts. This adaptability not only saves time but also significantly reduces the financial burden associated with setting up and operating an independent laboratory.
Besides, under the guidance of Dr. Rinat Borenshtain-Koreh and her team of experienced researchers, clients receive unparalleled support throughout the discovery process. From conceptualization to investor presentations, Da-Ta Biotech’s expertise ensures that promising drug candidates are not only identified but also meticulously developed to meet stringent industry standards.
By integrating in vitro cell-based assays into the drug discovery pipeline, Da-Ta Biotech significantly contributes to the advancement of medical science. Their comprehensive testing capabilities, combined with a client-centric approach, position them as an invaluable partner in the quest to bring innovative treatments from bench to bedside.
Significance in Toxicity Testing
In vitro cell-based assays have become indispensable tools in toxicity testing, offering a myriad of advantages over traditional in vivo methods. These assays employ either human or rodent cell lines, providing a controlled environment to assess the harmful effects of substances on living cells. Da-Ta Biotech, with its expansive repertoire of cell lines and disease models, stands at the forefront of this transformative approach.
Toxicity testing is critical in evaluating the safety of drugs, chemicals, and cosmetics. It determines the risk associated with exposure and helps in establishing safe dosage levels. Traditional methods, reliant on animal testing, have faced ethical, cost, and scalability challenges. In vitro cell-based assays address these issues, offering a more humane, cost-effective, and high-throughput alternative.
Da-Ta Biotech’s in vitro cell-based assay platforms help the screening of substances for cytotoxic effects. With over two dozen human and rodent cell lines, the company can simulate various physiological conditions and disease states. This capability is particularly beneficial for identifying toxic compounds early in the drug development process, potentially saving both time and resources.
The EC50 model, that is utilized by XTT, MTT LDH kits and many additional detection methods, is a standout feature in Da-Ta Biotech’s toolkit, exemplifies the utility of in vitro assays in toxicity testing. It measures the concentration of a substance required to produce a halfway maximal effect, providing critical information on the drug’s potency and safety margin. Similarly, the wound healing model offers insights into the regenerative potential of compounds, including their possible cytotoxic effects on growth and repair mechanisms.
By leveraging these sophisticated in vitro models, researchers can gather detailed toxicological data without the ethical and logistical complications of animal testing. Da-Ta Biotech’s commitment to providing tailored support, from conceptualization through to development, ensures that their clients can navigate the complexities of toxicity testing with confidence. The shift towards in vitro methods marks a significant advancement in ensuring the safety and efficacy of new compounds, with Da-Ta Biotech playing a pivotal role in this evolution.
Future Prospects and Advancements
In the constantly evolving world of biotechnology, in vitro cell-based assays are poised for significant advancements. As researchers and companies like Da-Ta Biotech continue to innovate, the future of these assays is bright, with new applications and technologies on the horizon.
One of the most exciting prospects lies in the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) within in vitro testing. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize how cell-based assays are conducted by predicting outcomes more accurately and rapidly than ever before. For example, AI algorithms can analyze data from cell-based assays to identify patterns and predict the efficacy of drugs with a high degree of accuracy. This would not only expedite the drug discovery process but also enhance the precision of toxicity and efficacy assessments.
Also, advances in 3D cell culture technologies are set to enhance the applicability of in vitro cell-based assays. Unlike traditional 2D cultures, 3D models more closely mimic the natural environment of cells within the human body, providing insights that are more reflective of in vivo conditions. This leap forward could dramatically improve the predictive value of preclinical testing, making it easier to identify potential issues before moving to human trials.
Besides, the expansion of cell-based assays to include more diverse cell lines, including patient-derived and disease-specific models, will allow for more personalized medicine approaches. By using cells that closely match the genetic makeup of specific patient groups, researchers can tailor treatments and screen for potential adverse reactions more effectively.
With companies like Da-Ta Biotech at the forefront, the field is also moving towards more sustainable and ethical research practices. The shift away from animal testing towards more reliable and humane in vitro methods is a significant advancement that aligns with growing regulatory and public demand for cruelty-free testing methods.
The push for broader adoption and standardization across the industry promises to make these powerful tools more accessible and reliable. As the capabilities of in vitro cell-based assays expand, their role in drug discovery and safety testing will only become more integral. Innovations in technology and methodology are set to open new pathways for research, paving the way for faster, safer, and more efficient drug development processes.
Conclusion
Da-Ta Biotech’s, innovative as well as classical, use of in vitro cell-based assays marks a significant leap forward in drug discovery and development. By harnessing the power of advanced biotechnologies, they’re not only streamlining the process but also paving the way for more personalized and ethical approaches to medicine. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of cutting-edge technologies like AI and ML alongside advancements in cell culture models will undoubtedly enhance the precision and speed of drug development. With companies like Da-Ta Biotech at the forefront, the future of drug discovery looks promising, offering hope for more effective and safer treatments.
At Da-Ta Biotech the sponsor’s research team can receive a complete hands-on service from the in-house team or get an access to Da-Ta biotech laboratory including performing the assay independently using the bench, Biohazard hood (BSL2), solvent chemical hood, Real-Tima PCR, ELISA reader, Luminometer, Fluorometer, Ultra centrifuge services, Anaerobic cell, Co2 incubator, Western blot system and Franz cells system. Companies that choose Da-Ta Biotech as a supplier get our team training, guidance and assistance timely and calibrated to fine tune just to the requested level.
Companies that require an assay, may ask for a literature review in order to choose correctly the in-vitro or ex-vivo model, set it up, calibrate and validate it. In those cases, a bank of scientific hours is applied that will further set the background for any proof of concept and rational.